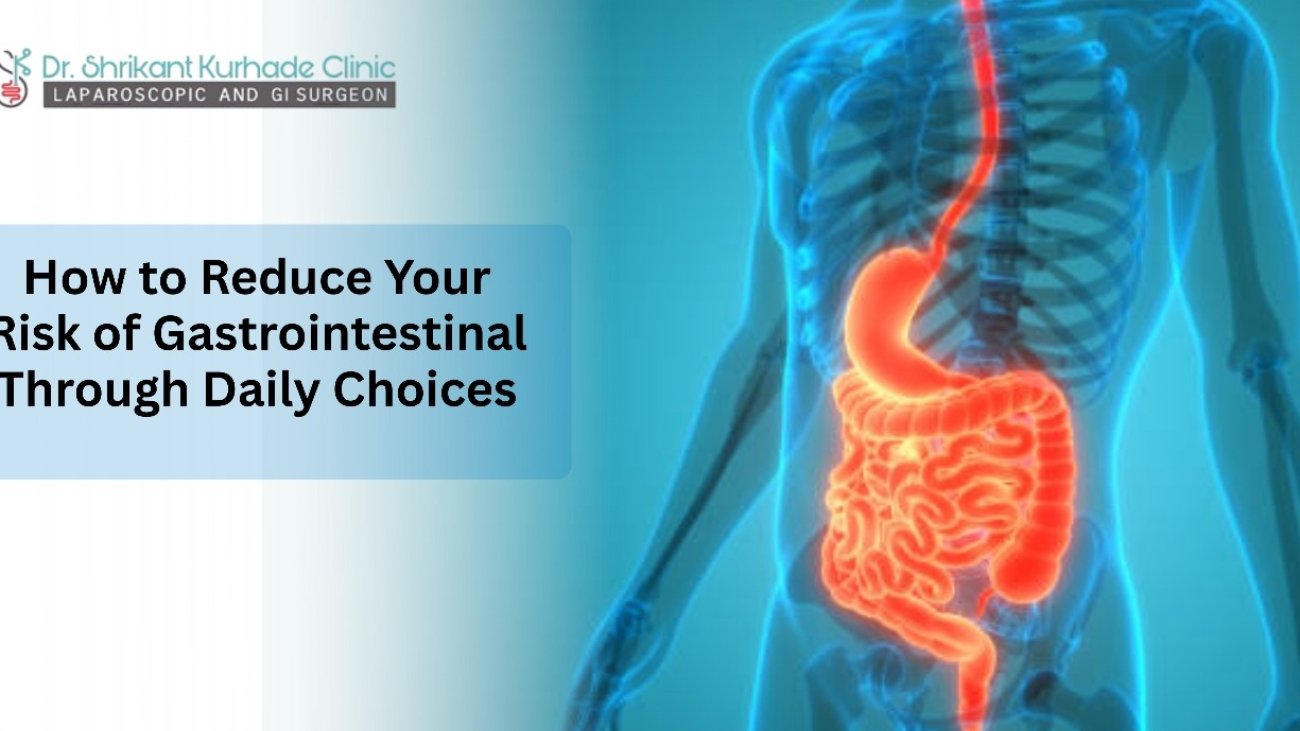
Your gastrointestinal (GI) system helps to remove waste, digest food, and absorb nutrients, hence contributing significantly to general health. However, poor lifestyle choices, bad nutrition, and stress can raise your chance of stomach issues including acidity, constipation, bloating, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and even more serious conditions including ulcers or colon disorders.
The excellent news is that making little, regular adjustments in your everyday schedule will greatly lead to a reduced risk of gastrointestinal issues and improve your overall digestive health. These are some efficient methods to protect your stomach by means of deliberate everyday decisions.
1.Eat a Fiber-Rich Diet
One of the most crucial nutrients for intestinal health is fiber. It promotes a healthy balance of gut flora, helps to control bowel movements, and avoids constipation.
- soluble fiber-Found in oats, apples, and beans, supports digestion and helps to reduce cholesterol.
- Insoluble fiber—found in whole grains, nuts, and vegetables—adds weight to stool and avoids constipation.
Every day, try to include fresh fruits, veggies, legumes, and whole grains in your meals. These are among the best foods for gastrointestinal health.
2. Stay Hydrated
Smooth digestion depends on enough water consumption. Dehydration can lead to constipation and sluggish bowel motions. Though personal needs can vary, adults should strive for 8–10 glasses of water on average every day. Good hydrating choices include herbal teas, coconut water, and soups as well. Proper hydration is one of the simplest healthy digestion tips you can follow daily.
3. Limit Processed and Junk Foods
Unhealthy fats, carbohydrates, and preservatives abound in packaged snacks, fried foods, and fast food. These foods can induce acidity, aggravate your digestive system, and promote obesity—a risk factor for several gastrointestinal disorders. Instead, choose home-cooked meals made with fresh and whole foods, which are vital for gastrointestinal disease prevention.
4. Practice Portion Control
Overeating can cause heartburn, bloating, or acid reflux by adding needless strain to your digestive system. Regularly consuming little, well-balanced meals maintains good digestion and stops pain. This is one of the easiest healthy stomach tips you can apply right away.
5. Manage Stress Levels
Gut health is directly affected by stress. Conditions like IBS, gastritis, or ulcers might worsen by anxiety and stress. By including stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, breathing exercises, or daily walks, you can dramatically lower your risk of gastrointestinal problems.
6. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity activates the intestinal muscles, guaranteeing regular bowel motions and lowering the chance of constipation. For at least thirty minutes daily, exercises like brisk walking, bicycling, or yoga can help to maintain your digestive system in good form. Regular movement is a natural way for how to improve digestion naturally.
7. Avoid Excessive Alcohol and Smoking
Both drinking too much alcohol and cigarette use damage the gastrointestinal system. They raise the risk of liver and colon illnesses, cause ulcers, and harm the stomach lining. One of the most effective actions you may do for your digestive system is to reduce or abandon these habits if you want to know how to avoid gastrointestinal problems.
8. Get Enough Sleep
Bad sleeping upsets the equilibrium of hormones controlling digestion and appetite. Strive for 7 to 8 hours of excellent sleep every night to help your body to mend and keep a good gut environment.
9. Include Probiotics and Prebiotics
Prebiotics food for good bacteria and probiotics good bacteria enhance the digestive system and gut flora. Foods like yogurt, kefir, buttermilk, bananas, garlic, and onions encourage a better gut environment and help lower the chance of stomach infections. Including them in your diet is an effective way for how to improve gastrointestinal health.
10. Practice Good Eating Habits
The way you consume is just as crucial as what you eat; modest habits can have a significant impact:
- Chew food thoroughly and gradually.
- Lying down right after meals should be avoided.
- Keep your mealtimes constant.
- Breakfast starts digestion, hence don’t miss it.
These simple healthy digestion tips can make a big difference.
11. Monitor Food Intolerances
Some individuals react badly to certain foods including gluten, dairy, or spicy cuisine. Ignoring these triggers might result in bloating, cramping, or diarrhea. Keep a food log to find foods that you should avoid because they bother your digestion. Understanding your triggers is an important step in gastrointestinal disease prevention.
12. Go for Regular Health Checkups
Early detection of gastrointestinal issues is made possible by preventive health examinations. See a gastrointestinal doctor for quick assessment if you often get symptoms such as chronic acidity, blood in stools, unexplained weight loss, or constant stomach pain. Preventive care is the best answer for how to prevent digestive problems before they become serious.
Conclusion
Daily decisions—what you eat, how active you are, and how well you control stress—determine your gut health. Avoiding processed foods, keeping hydrated, eating a fiber-rich diet, and regular exercise are basic lifestyle choices that can go a long way in avoiding digestive problems.
Dr. Shrikant Kurhade, a leading laparoscopic and Robotic Surgeon in Pune, offers patients with gastrointestinal problems specialized advice and cutting-edge treatment at KK Care Clinic. You can be sure of the correct diagnosis, customized care, and long-term digestive health thanks to his experience and patient-centered approach.
Manage your gut health today by making good daily decisions and visiting KK Care Clinic to see Dr. Shrikant Kurhade for expert gastrointestinal treatment.